Welcome to lesson 2 of our SEM tutorial – this time we aim to give you more insight into Pay-Per-Click advertising (PPC).
Now that you know the basics of SEO (we’ll assume you’ve read our previous blog because we poured our hearts and souls into writing it) has a longer-lasting effect on business visibility online, it could take months before you start seeing results. There aren’t any shortcuts to appearing as a top result on a SERP, however a proper PPC (Pay-Per-Click) strategy allows you to appear in the sponsored section of SERPs relatively quickly.
If this thought popped into your head: “What is PPC?”, then we’ve read your mind and apologise for doing so without your permission. PPC advertising entails bidding on relevant keywords your main audiences would search and just as the name suggests every time your audience clicks on a sponsored result, you are charged a price. The bid or price you are charged is dependent on the assigned budget, the competition (Low, Medium, High) and monthly searches for the targeted keywords.

How does PPC work?
1. Choosing the Right Keywords
Keywords can be divided into two categories: short-tail and long-tail keywords. Short tail keywords are short ones with only a few words, not too specific phrases that people search, like – ‘digital marketing’. Whereas long-tail keywords are much more specific and longer phrases, such as – ‘why is Fortune Media so good at digital marketing’(*wink wink*).
Choosing the right keywords is the first step to building your PPC campaigns. The keywords can be chosen based on your business, your customers, your services and products, your industry or your environment. There are several tools that can help find the right set of keywords for your campaigns:
2. Creating the ads
When it comes to SEM there are two main types of PPC ads:
– Paid Search Ads:
These types of ads appear first on the SERPs. They are commonly text ads comprised of three key parts: headline text, display URL, and description text. In the case of Google you can have additional extensions on your ads to provide more information to the users. You can include links to different pages on your site, callout, call or click to text extensions.
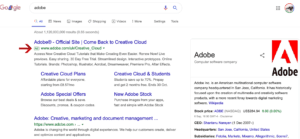
– Google Shopping Ad
These types of ads serve best for e-commerce businesses. They display an image of the advertised product, a headline text, the price, your shop and the name of your business. These ads are extremely appealing to users, in 2018 they accounted for 60% of clicks on Google, and depending on your type of business they should be an integral part of your PPC strategy.
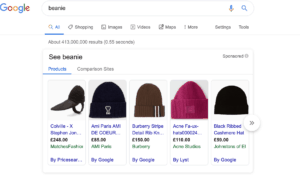
3. Building the Ad Campaigns
There are a lot of different strategies a business can implement when building an ad campaign that targets the chosen keywords. And based on those strategies you can choose from different types of campaigns:
- Generic Campaigns
- Brand Campaigns
- Competition Campaigns
- Location Campaigns
Let’s say your business is a clothing store in East London, that specialises in winter wear called Le Petit Coat. A Generic campaign would consist of writing ads that target generic searched-for keywords like ‘winter wear store’ or ‘stores that sell jackets’. Brand campaigns would target keyword terms involving your brand name – like ‘Le Petit Coat clothing store’. Competition campaigns would focus on targeting… wait for it… that’s right your competitors brand (of course there are certain rules in place when you use this type of campaign). Lastly, Location-based campaigns would target keywords using specific locations ‘clothing stores East London’.
4. Quality Score
Each ad you create will have a Quality Score determined by the search engine. The Quality Score is an estimate of the quality of your ads, keywords and landing pages. The higher your Quality Score the better your ad will rank and the lower the cost you’ll need to. Quality Score is based on a scale of 1 to 10.
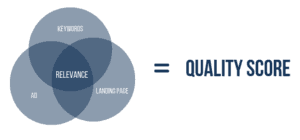
To improve the Quality Score of your ads you’ll need to focus on the relevance of your ads in relation to your target audiences and their experience on the landing page.
PPC can drive traffic to your site and deliver leads and faster than SEO, but the downside is that it’s dependent on your marketing budget. Whereas SEO is a long-term strategy that keeps working as long have a comprehensive SEO strategy in place.
So, if you’re asking yourself SEO vs PPC which should I choose? (there we go again, reading your mind) We can only say: you need both! A good SEM strategy will use the different channels and tools to increase the visibility of your brand and product/services online. Stay tuned for our SEM lesson 3 on explaining the differences between them.
If you’d like some help with your SEM strategy to be sure to get in touch with us or if you’re looking for other ways to improve your business come by for a cuppa and we can help you out.


